Authentication Settings
Companies maintain a store of users and their details. EMM provides a mechanism to either create a store of users in EMM
Local Directory
The Local Directory is available by default within EMM. It is a directory of all users created on EMM only by using the Add User. Local users are stored in EMM database.
Active Directory (AD)
ADs are external sources of users. Active Directories are only third party sources for EMM.
Important: As an administrator, you must have the appropriate permissions to configure multiple Active Directory instances.
Once you have logged into the Management Console, from the left pane, click the Authentication Settings under the Settings. The Authentication Settings page appears with a list of Directories configured within EMM. You can search ADs.
The Directory List view displays the following columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Domain | Displays the list of AD domains. |
| Directory Type | Displays the directory type of the AD. |
| Host or IP Address | Displays the list of host names or IP addresses. |
| Port | Displays the port numbers of the Active Directory Servers. |
| Created By | Displays the name of the administrator who created the configured Active Directory Servers. |
| Created On | Displays the date and time details of when Active Directory Servers configured. |
Information Icon |
Displays the number of users and groups imported from the Active Directory when you click on the information icon. If no users or groups are imported from a Directory, the information icon turns into a check box. If you want to delete an Active Directory, you must select the desired check box and then click the Delete button. |
| Delete button | Deletes the selected Active Directory from the database. The Delete button dims because it is not available until a check boxes is selected. |
You can navigate the list view through the Previous and the Next buttons.
Active directories help ensure that only authenticated users and computers can access the network. These upcoming sections will help you learn more about managing your network resources:
- Configuring Active Directory
- Configuring an AD with a Secured VPN for Management Cloud
- Searching and Filtering Active Directory
- Viewing Number of Users/Groups Imported from AD
- Updating Active Directory
- Deleting Active Directory
Configuring Active Directory Settings
The Authentication Settings page is used to configure communication between EMM database and an AD. The EMM Console uses database to fetch employee details, to provide user authentication, and to update and synchronize users.
Once you have logged into the Management Console, under Settings from the left pane, click Authentication Settings. The Directory List page appears. Click the +New Directory button. The Authentication Settings page appears with directory list. Click on any of the directory, the Directory Details page appears with two tabs: Configuration and Synchronization.

Configuration Tab
There are two types of ADs can be configured:
- Forest
- No Forest
A Forest AD can have multiple sub-domains under the same. A No Forest AD on the other hand has only one domain associated with it.
To configure the ADs, follow these steps:
- Select the Directory Type. By default this is set to No Forest. If you want to configure Forest AD, go to Step 2 in the below procedure and continue, else skip to Step 3 to continue with No Forest AD.
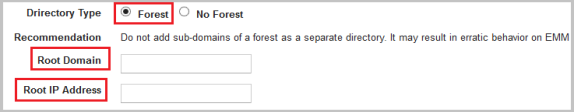
- Click the Forest option if you want to configure for the Forest AD.
The system displays the Root Domain and the Root IP Address fields.
Following are the three types of groups of Forest ADs:
- Universal: These Groups are universal across entire forest. When the Group type is universal, the system imports all user references into EMM while importing users from the group.
- Global: When the Group type is Global and if it belongs to a sub-domain, the system does not import the user references while importing users from it.
- Domain Local: If the Group type is Domain Local and if it belongs to a sub-domain, the system does not import the user references while importing users from it.
In case of Forest AD configuration, not all Groups can be imported (with User association in tact). Only Universal Groups can be imported from sub-domains. From root domain, all Groups can be imported.
- Universal: These Groups are universal across entire forest. When the Group type is universal, the system imports all user references into EMM while importing users from the group.
- Type the required domain details:
Important: Do not add sub-domains of a Forest as a separate directory. While synchronizing Users and Groups, if common Users and Groups are found, it may result in erratic behavior.
If directory type is Forest AD, follow these steps:- Root Domain: Enter the Root Domain name of the Forest AD.
- Root Host Name or IP Address: Enter the Root Host Name or IP Address of the Forest AD.
Or
If directory type is No Forest AD, follow these steps:
- Domain: Enter the Domain name of the AD.
- Host Name or IP Address: Enter the Host Name or IP Address.
Note: If you are configuring AD for Management Cloud, you need to configure a secure VPN for Cloud. To configure an AD with a Secured VPN for Cloud, refer to Secured VPN for Cloud.
- Enter the required server connection details:
- Port Number: Enter the port number of the AD Server.
Refer to the Note at Require Secure Connection field for default and recommended ports. You may choose to provide your own ports.
- Login Attribute: Select one of the attributes from the drop-down list to search AD.
- User Name: Enter the user name that is used to access the EMM server.
- Password: Enter the password that is used to access the EMM server.
- Search Base: Enter the domain context.
A Domain Context is a client-side representation of a domain service, providing access to all the functionality of the service. - Require Secure Connection: By default, this is configured to No. Click Yes if you wish to enable secure connection using LDAPS.
The port numbers are vary based on configuration. The system displays default and recommended port numbers as follows:Directory Type If Secure LDAP = No If Secure LDAP = Yes No Forest 389 636 Forest 3268 3269
For No Forest, if no context is specified, the system searches all Users from the root of AD by default. If you want Users to be searched from a specific node of the AD, specify the context. All searches shall happen form this context only.
For Forest, the Context field is used for Test Connection only. It is a non-mandatory field. If unspecified, the default context is the root domain. All live searches (non-test connection) happen from the root domain only.
- Port Number: Enter the port number of the AD Server.
- Click the Test Connection button. If the connection is established, a confirmation message appears.
-
Click the Save button.
Save status message appears.
- Click OK to return to the main page.
Important: In this application, wherever passwords need to be provided, some browsers may ask to Remember Password. Opt for Never as it is irrelevant. Your enterprise passwords should not be remembered
Synchronization Tab
Once communication with ADs are configured, admin can configure synchronization of ADs based on time, days or weekly basis to get the latest information of Users or any newly added Users.
Synchronization can be done in one two ways:
- Sync Timings: admin configures sync jobs.
- Sync Details: admin initiates this process manually.

To configure the synchronization, follow these steps:
- Synchronization Start Time: Place cursor in Synchronization Start Time field.
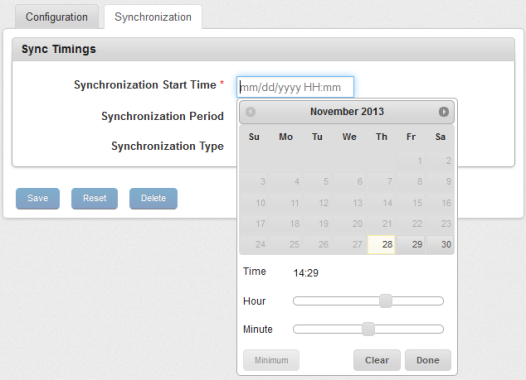
The Calendar appears.
- Select the Date and Time (Hour: Minute) and click Done.
The selected Date and Time appears in the field.

- Synchronization Period: Select the synchronization period from the drop-down list.
- Custom Period: Select the one of the options to customize the sync job based on Hours, Days, or Weeks.
- Synchronization Type: By default, this option is set to Imported. This option synchronizes users who are imported into the EMM database.
- Click the Save button. In the success message that appears, click OK to return to the main page.
Note: If an already
Sync Details
- Click one of the buttons for Directory Sync Status.
Directory Sync Status: If the sync job is in progress, the system displays the status as "Synchronization in Progress".Note: If a sync job in progress, the Sync All and the Sync Imported buttons will be inactive.
- Sync All: Click this button to synchronize all Users from the Directory.
- Sync Imported: Click this button to synchronize only imported users from the Directory.
Last Directory Sync Start Time: Displays the last Directory sync when started.
Last Directory Sync Completed Time: Displays the last Directory sync when completed.
Next Directory Sync Start Time: Displays the next Directory sync when scheduled.
- Click the Save button. In the success message that appears, click OK to return to the main page.
Filtering Active Directories
You can search desired AD through the available search filters. You can apply a single or a combination of search filters to define the search criteria and get the refined outcome.
The Admin can click on the one of the table headers. Based on the sorted element, the system sorts the entire directory list to either ascending or descending order. The system displays an indicator to show if the sort is in ascending or descending order.
If the sort is in ascending order, the sort order is Numeric [0-9], Alphabetic [a-z, A-Z], Special characters.
Admin can also manually sort on the basis of all columns.
Filtering
Admin can enter text in the text fields to filter the column. The text must be at the beginning of each word of the column entry.
The system will filter all elements of the column based on the search term present in the column.
For example, If Admin types "Herm" or "herm", and presses the Enter key, then the system displays all directory names that contain herm. For example, Herman Melville, Herman Schultz, Kermit Hermit and Sherman.
The following columns have textual filters:
- Domain
- Host or IP Address
- Port
Filtering from Drop-down list
An administrator can filter data by one of the following options:
- Created By
- Created On
| Filter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Created By:
|
The server only displays those directories (rows) that have the filtered entity.
Filters can be applied for one or more columns. If filters are applied across multiple columns, the system performs AND condition between all filters.
|
|
Created On:
|
You can specify dates and time with the Created On filters. The filters represent data based on the following:
All the above ranges are non-overlapping and ensures that no results are double counted. |
Viewing Number of Users or Groups Imported From an Active Directory
From the Directory List page, you can view the details on how many users and groups are imported.
Note: When there are no users or groups imported from an Active Directory (AD), the information icon turns into a check box. To delete an AD, you select the desired check box and then click the Delete button.
To view the details, click the information icon next to Domain column. The system displays the details of users and groups imported from the AD.

You can click anywhere outside of the dialog to close it.
Updating Active Directory Settings
You may need to update an AD settings for specific reasons, for example, you may need to update a port number or its search base.
From the Directory List page, click one of the AD in the Domain column.

The Directory Settings page appears.
The desired fields can be updated. There are no restrictions. Once an AD is updated, it must be saved again to come into effect.
Deleting Active Directory
To delete an Active Directory, imported Users and Groups of the active directory should be deleted first. To delete all users and groups from an active directory, an admin can either use the bulk action feature from the Users and Groups pages or the admin can use the Purge button on the pop-up box after clicking the Information icon. Following either action, when no more users or groups from a particular AD have been imported into EMM, the Information icon changes into a checkbox and the AD can be deleted.

Note: When there are no Users and Groups imported from that AD, only then the Information icon turns into a check box.
To delete a Directory, follow these steps:
- Select the check box for an AD entry next to the Domain.
- Click the Delete button.
The system displays Delete Directory Confirmation Message: "The chosen Directories shall be removed from the Directory list. Are you sure you want to do this?"
- Click Yes to confirm the deletion. The Directory is removed from the list.
SAP Directory
Kony Fabric Identity
Kony Management suite helps you to delegate Enterprise Store user authentication to Kony Fabric Identity service. Kony Fabric Identity service is part of Kony Fabric that validates users accounts and applications for authentication and authorization.
Kony Management suite allows administrators to configure Kony Fabric Identity service. Kony Management suite supports Kony Fabric Identity service as an alternative authentication mechanism only for the Kony Management Enterprise Store log-in.
Support is not provided for the following authentication scenarios.
- EMM Management Console
- EMM Self Service Console
Users authenticated through Kony Fabric Identity service are mapped to existing users in Kony Management. If a Kony Fabric Identity service user does not exist in Kony Management server, the user is created in Kony Management Suite. When you set the Kony Fabric Identity service authentication for the enterprise store, based on your Kony Fabric Identity service provider configured, you will be redirected to your Kony Fabric Identity service authentication page
The following are the identity providers supported by Kony Fabric Identity Service in Kony Management Suite:
- OAuth 2.0
- CA SiteMinder
- Microsoft Active Directory
Important: Kony Fabric Identity service is supported only for iOS and Android devices.
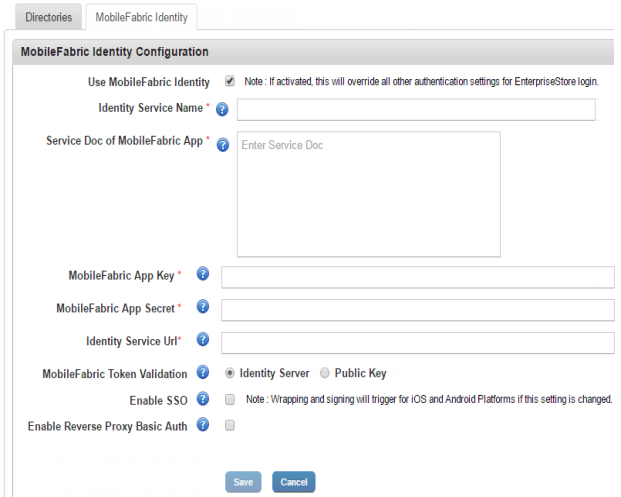
Kony Fabric Identity tab displays the following:
Kony Fabric Identity Configuration
- Use Kony Fabric Identity: When you select the feature, rest of the fields in the Kony Fabric Identity tab appear.
- Identity Service Name: Enter the Identity Service name that the Enterprise Store should use to authenticate the user. You can obtain the service name from the Publish screen by clicking the Key icon after the app is published to the server.
- Kony Fabric App Key: Enter the App key of the Kony Fabric back-end app that your Enterprise Store uses for authentication. You can obtain the app key from the Publish screen by clicking the Key icon after the app is published to the server.
- Kony Fabric App Secret:Enter the App secret of the Kony Fabric back-end app that your Enterprise Store uses for authentication. You can obtain the app secret from the Publish screen by clicking the Key icon after the app is published to the server.
- Identity Service URL: Enter the service URL of the Kony Fabric back-end app that your Enterprise Store uses for authentication. You can obtain this from the Publish screen by clicking the Key icon after the app is published to the server.
- Service Doc of Kony Fabric App: Enter the Service Doc details of the Kony Fabric back-end app that your Enterprise Store uses for authentication. You can obtain the service doc details from the Publish screen by clicking the Key icon after the app is published to the server.
- Kony Fabric Token Validation: Select the Kony Fabric token validation method, either with a preconfigured Kony Fabric Server or a public key.
- Public Key : Enter the Public key details. The following two fields appear.
- Trust Auth URL: Enter your Kony Fabric Tenants URL details.
- Trust Auth Cert: Enter your Kony Fabric Tenants certificate details.
- Identity Server: Select the option to validate your Kony Fabric Token using your Kony Fabric identity server details. Your Kony Management environment must already be configured in your Kony Fabric server. For more details, click here.
- Public Key : Enter the Public key details. The following two fields appear.
- Enable SSO:Select the option to use single sign-on for apps built using Kony Fabric SDK.
- iOS Keychain Group: Enter iOS keychain group details.
- Android Broadcast Passphrase: Enter the passphrase for Android broadcast.
Note: For iOS, multiple SSO groups are not supported.
Note: If a child app exists before configuring Kony Fabric identity service settings, the child app must be re-wrapped.
Note: When a child app is re-wrapped, the entitlement.plist file is overwritten, and some features (for example, In app purchase) may not work.
Note: While using OAuth 2.0 for SSO, if you click on Forgot Password button and then return to the Login page to log in, you cannot log in to the Enterprise store. You need to kill the Enterprise store on your device and relaunch it.
- Enable Reverse Proxy Basic Auth: Selecting the option enables reverse proxy basic authorization. If your Kony Fabric Identity Server is behind a proxy server (for example CA SiteMinder), which needs basic authentication, select this option.
- Save: Click this to save the details you enter on the page.
- Cancel: Click this to cancel the changes you make on the page.
Note: If you change AppKey, AppSecret, and Use SSO settings, for iOS and Android platforms, wrapping will be triggered for Enterprise Stores.
How to Configure Kony Fabric Identity Settings
To configure Kony Fabric Identity settings, do the following:
- In the Management Console, under Settings, click Authentication Settings. The Authentication Settings page appears.
- Click the Kony Fabric Identity tab. The Kony Fabric Identity tab opens.
- Select Use Kony Fabric Identity. More options appear.
- In the Identity Service Name field, enter a service name.
- In the Service Doc of Kony Fabric App field, enter the service doc details.
- In the Kony Fabric App Key field, enter the app key.
- In the Kony Fabric App URL field, enter the URL value.
- From Kony Fabric Token Validation, select an option.
- If you want to enable SSO, select Enable SSO.
- In the iOS Keychain Group, enter the iOS keychain group name.
- In the Android Broadcast Passphrase field, enter the passphrase for Android broadcast.
- Select Enable Reverse Proxy Basic Auth to enable reverse proxy basic authorization.
- Click Save. A confirmation message appears.
- Click OK.
For more information on Kony Fabric Identity service, click here.
For more information on Kony Fabric Identity App Key, App secret, and Service Doc, click here.
| Rev | Author | Edits |
| 4.1 | PK | PK |
| 4.2 | PK | PK |
| Copyright © 2018 Kony, Inc. All rights reserved. |
