Local Authentication API
The Local Authentication API enables validation of credentials in iOS and Android applications. The kony.localAuthentication Namespace provides APIs for various authentication modes. Currently, the namespace supports the Touch ID and Face ID modes of authentication.
Touch ID is a biometric fingerprint reader that enables users to unlock the device, authenticate various payments, and so on. Touch ID is stored securely in the device and is not accessible outside. The Touch ID feature is available in the iOS from iOS 8 onwards and in the Android from Android M onwards.
Face ID is an iOS-specific facial recognition system that acts as the successor to Touch ID. This authentication mechanism allows biometric authentication to unlock a device, make payments, and access sensitive data. Furthermore, Face ID provides detailed facial expression tracking for Animoji and other features. Face ID was initially released with the iPhone X, but this mechanism has since been updated and introduced to all the latest iPhone and iPad Pro models.
Note: For information about how to enable the Face ID feature in your Kony Visualizer application, click here. For information about how to detect whether a device supports either the Touch ID or Face ID feature, refer the getBiometryType API.
The Local Authentication API contains the kony.localAuthentication Namespace and the following API elements.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
kony.localAuthentication.authenticate
|
Authenticates the user. |
kony.localAuthentication.getBiometryType
|
Differentiates whether a device supports either the Touch ID or Face ID feature. This API is available from iOS 11. |
kony.localAuthentication.cancelAuthentication
|
Cancels the current authentication process. |
kony.localAuthentication.getStatusForAuthenticationMode
|
Returns the status of the authentication mode. |
To find the mode of local authentication supported by your device, use the kony.localAuthentication.getBiometryType function. Use the touch ID or face ID feature and then find the state of authentication mode by using the kony.localAuthentication.getStatusForAuthenticationMode function. You will receive a status code indicating support for the local authentication. After you get the success status code (5000), you can now authenticate the user by using the kony.localAuthentication.authenticate function. If you want to cancel the authentication process, you can use the kony.localAuthentication.cancelAuthentication function.
| iOS | Android |
|---|---|
|
|
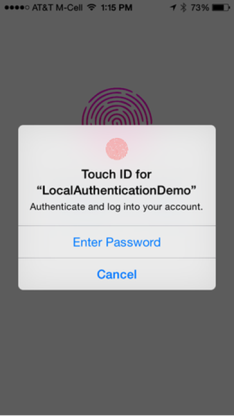
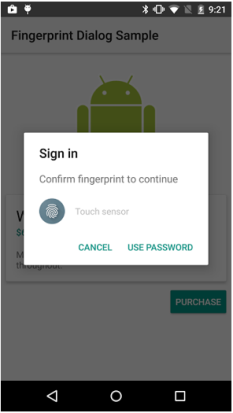
In the above illustrations, a dialog box is prompted to authenticate the user to use the app. User can choose to authenticate either by fingerprint or by password. User will be authenticated by touching the Touch ID with the registered fingerprint. If the user clicks the Enter password button or the USE PASSWORD button respectively, the user can authenticate using the registered password.
In the iOS devices, the dialog box is prompted automatically by the platform itself, where as in the Android devices, the dialog box is a custom UI; you have to design and build the custom logic as per your requirement.
Users need to register fingerprint at the global settings, and the same secured data is accessed from application to authenticate. You can also set a password at the application level, which acts as an alternative method for authentication.
To use the local authentication feature in the Android platform, you need the USE_FINGERPRINT permission set to true under the Manifest Properties in the Project Settings>Native>Android tab.
Note: The applications that use the kony.localAuthentication APIs must be in the foreground. If an application uses kony.localAuthentication APIs, the application should handle errors and respond properly with the UI to ensure an alternative method for logging on to the application.
| Rev | Author | Edits |
| 7.1 | NC | NC |

| Copyright © 2013 Kony, Inc. All rights reserved. |